spore vials
do mushroom spores need air to grow after harvest ?
Examining the Link Between Air and Successful Mushroom Spore Production After Harvest
Introduction
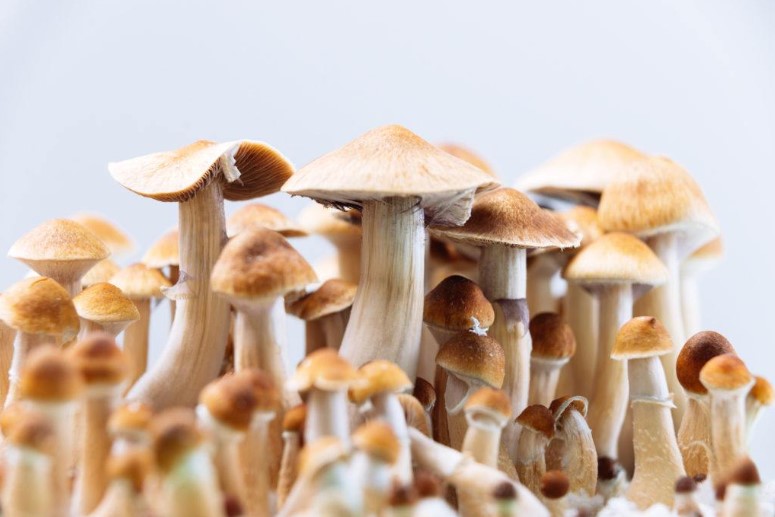
Mushrooms are a type of fungus that reproduce by releasing spores into the air. These spores, which look like tiny grains of sand or dust, are an important part of mushroom reproduction as they carry the genetic material needed for new mushrooms to grow. While some mushrooms can release their spores without any assistance from humans, spore production after harvest is often necessary in order to obtain enough viable and healthy spores to start a successful crop. Therefore, it is essential to understand how air affects the growth of these delicate organisms after they have been harvested.
The first step in understanding this process is becoming familiar with what exactly mushroom spores are and why they require air for successful germination after harvesting them. Mushroom spores contain the genetic information needed for reproduction but cannot thrive on their own; instead, they must be exposed to certain environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity in order to properly mature and germinate once harvested. Additionally, air plays an important role as oxygen helps activate enzymes within the spore which help facilitate its development into a new organism. Without adequate air circulation during this period, many mushroom species may struggle to produce viable offspring following harvest.
Mushroom Reproduction
In order to ensure that spores are able to germinate successfully after harvest, growers must provide the correct environmental conditions for them. This includes providing enough oxygen and maintaining a consistent temperature and humidity level. Oxygen is particularly important as it helps activate enzymes within the spore which help facilitate its development into a new organism. Without adequate air circulation during this period, many mushroom species may struggle to produce viable offspring following harvest.
The amount of air needed by mushroom spores also varies depending on the type of mushroom being grown. For example, some mushrooms require higher levels of oxygen while others need less in order to be successful. Additionally, different species have different ideal temperatures and humidity levels which must be maintained for optimal growth; if these requirements are not met then the spores may fail to germinate or develop properly leading to poor yields from your crop. Therefore, understanding what types of mushrooms you’re growing and their specific needs is essential for ensuring good results post-harvesting.
Once an environment suitable for spore germination has been created, growers can begin harvesting their crops when they reach maturity. Careful attention should be paid during this process as mishandling or over-harvesting can cause damage that will prevent proper spore reproduction in future cycles. Once harvested correctly however, growers can store their mushrooms in breathable containers such as paper bags or mesh sacks until ready for use; this ensures that they receive ample amounts of oxygen without becoming too moist and allowing mold or fungi growth which would contaminate your product with unwanted microbes!
Harvesting Mushroom Spores
When harvesting mushroom spores, it is important to take several factors into consideration. First and foremost, the timing of the harvest must be carefully planned to ensure that the mushrooms are mature enough for spore production. Generally speaking, most species will reach full maturity in around two weeks after pinning, however this time frame can vary depending on environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity. Additionally, while some types of mushrooms may produce viable spores without assistance from humans, others may require physical stimulation such as shaking or brushing in order to help release them into the air.
Once ready for harvest, it’s important to use gloves during collection as contamination can easily occur if exposed skin comes into contact with any part of the fungus; additionally this helps prevent accidental inhalation of any airborne spores which could cause respiratory irritation or infection. When collecting your crop it is also a good idea to place harvested mushrooms in breathable containers such as paper bags or mesh sacks until ready for use; this ensures that they receive ample amounts of oxygen without becoming too moist and allowing mold or fungi growth which would contaminate your product with unwanted microbes!
Finally, once you have collected all necessary materials needed for spore production it’s time to dry out your mushrooms before storing them away safely; generally speaking drying times range anywhere between one day up to a week depending on species type and environmental conditions so make sure you keep an eye on progress along every step! Once dried properly these mushrooms should remain viable for many years provided they are stored correctly in sealed plastic bags away from direct sunlight or other sources of heat/humidity. Following these simple steps will guarantee success when harvesting mushroom spores ensuring maximum yields every cycle!
Preparing and Growing After Harvest
Once the spores have been harvested, it is important to prepare a suitable growing environment for them in order to ensure successful germination. This includes providing adequate air circulation as oxygen helps activate enzymes within the spore which help facilitate its development into a new organism. Additionally, different mushroom species require specific temperature and humidity levels in order to thrive; if these requirements are not met then the spores may fail to germinate or develop properly leading to poor yields from your crop. Therefore, understanding what types of mushrooms you’re growing and their specific needs is essential for ensuring good results post-harvesting.
When preparing the substrate for growth after harvest, growers should also consider how they will provide water for their newly germinated mushrooms. Generally speaking, most species need access to moisture in order to survive and grow; however this can be done either through direct watering or by using a terrarium with high humidity levels such as those found in greenhouses or indoor grow tents. Additionally, some species may require additional nutrients such as nitrogen or phosphorus added directly into the soil so read up on any special requirements before planting!
Finally once your substrate is ready it’s time for planting! Depending on your chosen method of propagation (e. g., plugs vs grain spawn), follow instructions carefully when placing spores into their new home; generally speaking most types prefer an even distribution across the surface area being used which helps promote even growth throughout your crop cycle! After planting make sure that you keep an eye out for any signs of contamination such as mold or mildew which could ruin all of your hard work – if left unchecked these organisms can quickly spread across entire crops leaving behind nothing but unusable product so take care during every step!
Preserving Spores After Harvest
Once the spores have been harvested, it is important to store and preserve them in order to ensure their viability and success when germinating. The best way of doing this is through refrigeration as this helps prevent excessive heat or cold from damaging the delicate spores. Additionally, storing the spores in airtight containers also ensures that they are protected from any external contaminants such as dust or mold which could spoil your crop before even getting started! When placing them into storage make sure you label each container clearly so you know exactly which type of mushroom species each one contains; this will help keep track later on when planting out your crop.
In addition to refrigeration, it is also important to protect your spores from temperature fluctuations during storage; large changes can destroy many types of mushrooms due to their sensitive nature so take extra care when handling them post-harvesting! To do this try keeping multiple containers with different temperatures within a single refrigerator – for example one at 4°C (39°F) and another at 10°C (50°F). This allows for a more stable environment while still providing enough oxygen for spore activation during germination. As an added bonus, labeling each container will allow you easily identify which type of mushroom species belongs where should there be any confusion down the road!
Overall preserving mushroom spores after harvest requires careful attention and preparation but if done correctly can yield incredible results. Through proper storage techniques such as refrigeration combined with environmental protection against sudden temperature swings growers can successfully save their precious crops for use later on ensuring maximum yields every cycle!
Common Problems and Solutions
Common Problems and Solutions
Mushroom growing can be a difficult yet rewarding process with numerous factors to consider in order to achieve the best possible results. However, no matter how experienced you are as a grower there will always be annoying little problems that pop up along the way. To help combat these issues here’s an overview of some of the most common mushroom growing problems encountered by growers and solutions on how to address them:
Poor Air Circulation – Without adequate air circulation, mushrooms may not receive enough oxygen for proper growth which can lead to stunted or malformed fruits; this is especially problematic when trying to cultivate indoors using limited spaces such as grow tents or greenhouses. To fix this try adding additional ventilation systems such as fans or humidity controllers which help maintain airflow while still providing necessary environmental conditions for your crop! Additionally, make sure that all equipment used is well maintained and any potential blockages are cleared out regularly in order to ensure optimal performance at all times!
Contamination – The presence of harmful contaminants such as molds or bacteria within a substrate can quickly ruin entire crops leaving behind nothing but unusable product; if left unchecked it could even spread across multiple batches making eradication nearly impossible without starting from scratch again. In order to prevent this problem from occurring regular sterilization should take place before each use either through chemical treatments such as bleach solution or heat pasteurization using steam/boiling water (depending on substrate type). Additionally, protective clothing should also be worn whenever handling materials in order to avoid cross-contamination between batches!
Substrate Issues – Substrates are what provide nutrition for your mushrooms during cultivation so if they contain too much moisture then fruit bodies may not form properly leading poor yields; alternatively if there’s not enough moisture then fruiting bodies may fail entirely due lack of nutrients needed for development. To fix this try adjusting p H levels within substrates via addition of
Conclusion
In conclusion, harvesting and growing mushroom spores can be a rewarding yet challenging process that requires careful attention in order to achieve the best possible results. By understanding what types of mushrooms you’re growing and their specific needs, preparing an adequate environment for them to grow in, providing water for germination as well as direct planting instructions you can ensure successful harvests every cycle! Additionally, through proper storage techniques such as refrigeration combined with environmental protection against sudden temperature swings growers are able to save their precious crops for future use ensuring maximum yields each time. With all these tips taken into consideration even novice growers should have no problem cultivating bountiful crops of delicious mushrooms!